How HTTPS works
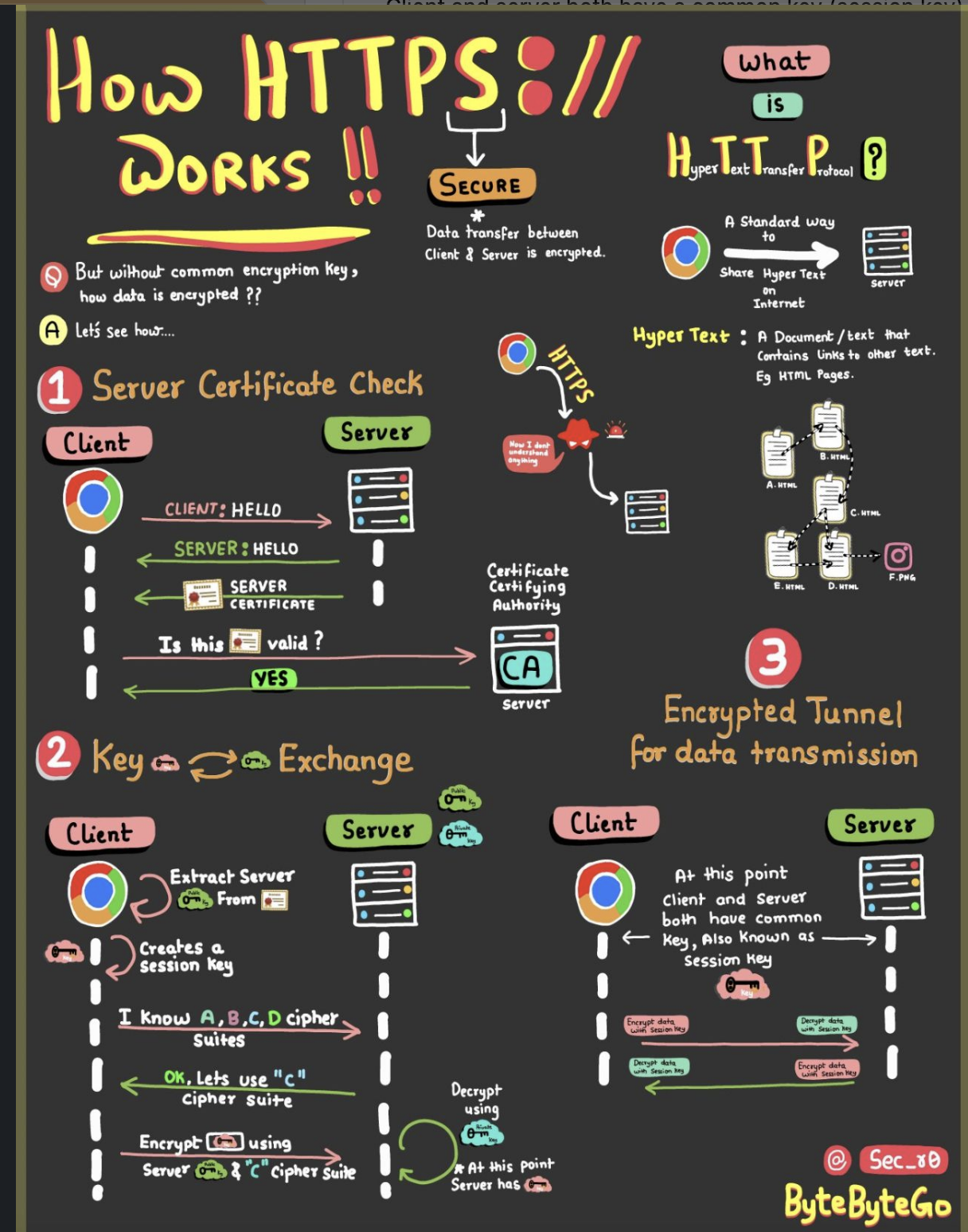
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is a secure way to share information on the internet. It encrypts data transfer between client and server.
But without common encryption key, how data is encrypted?
Let's see how:
1 - Server Certificate Check
- Client and server exchange "HELLO" messages
- Server sends its certificate
- Client verifies it with a Certificate Authority
2 - Key Exchange
- Client extracts server's public key, creates a session key
- They agree on a cipher suite
- Client encrypts session key using server's public key
- Server decrypts it
3 - Encrypted Tunnel for data transmission
- Client and server both have a common key (session key)
- They use it to encrypt and decrypt data during transmission
This creates a secure, encrypted tunnel for data transfer, protecting information from eavesdropping and tampering.
No comments:
Post a Comment